GST Return Filing
Legal Kamkaj provides easy and quick services for getting a GST Return Filing? If so, you should know that a GST Return Filing plays an absolutely crucial role in, in fact, assisting businesses—particularly those navigating the complex and, at times, daunting process of filing Goods and Services Tax (GST) returns. Specifically, a GST Return Filing offers expert and invaluable guidance on the necessary documents, strict deadlines, and specific forms required for compliance.
Furthermore, with their extensive expertise and deep understanding of the GST framework, a GST Return Filing ensures that businesses, without a doubt, accurately report their sales, purchases, and tax liabilities. As a result, this diligent process helps businesses avoid potentially severe penalties and, importantly, ensures timely submissions—something that is essential for maintaining good standing with tax authorities. Moreover, by working closely and collaboratively with a GST Return Filing , businesses can not only save a significant amount of time but also, quite importantly, significantly reduce their stress levels. Consequently, this ultimately allows business owners to focus on their core operations while, at the same time, staying fully compliant with GST regulations.
In summary, if you are indeed looking for a reliable and trustworthy GST Return Filing , partnering with one can be immensely beneficial for your business. You will find that their expert support can lead to a much smoother filing process, ultimately contributing to the overall success and growth of your business
Get Started GST Return Filing?
GST Return Filing - An Overview

Filing GST returns, without a doubt, is an essential compliance procedure where businesses, in fact, report their transaction details and tax information. Consequently, it ensures a structured approach to managing the GST system, which is, ultimately, crucial for maintaining regulatory compliance.
Specifically, GST return filing entails, among other things, providing comprehensive data on purchases, sales, GST collected on sales (often referred to as output GST), and, furthermore, the input tax credit (ITC) for purchases. All businesses, regardless of their size, that are registered under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Act of 2017 are, therefore, required to file returns on a monthly, quarterly, or, in some cases, an annual basis. These returns, in turn, provide a summary of GST invoices, receipts, payments, and other relevant financial transactions that are integral to accurate accounting.
Moreover, to avoid any potential penalties, it is essential that businesses submit their GST returns within the designated deadlines. By adhering to these deadlines, businesses not only ensure compliance but also maintain a good standing with the tax authorities, which is, ultimately, beneficial for their overall operations.
In summary, filing GST returns is a critical process that helps businesses manage their tax obligations effectively while ensuring transparency and accountability in their financial dealings
Benefits of GST Return Filing
Legal Compliance
- Helps businesses comply with tax laws and avoid penalties for non-compliance.
- Ensures proper documentation and reporting of business transactions.
Input Tax Credit (ITC) Claim
- Allows businesses to claim Input Tax Credit on purchases, reducing the overall tax burden.
- Ensures seamless tax flow and prevents cascading tax effects.
Better Business Credibility
- A properly filed GST return builds trust with customers, vendors, and financial institutions.
- Helps in obtaining loans and government tenders, as GST compliance is often a requirement.
Seamless Business Operations
- Enables smooth inter-state and intra-state trade by ensuring businesses are tax-compliant.
- Necessary for e-commerce sellers and businesses engaged in digital transactions.
Avoidance of Penalties
Late or incorrect filing can attract heavy fines and penalties. Timely filing helps avoid unnecessary financial liabilities.
Easy Processing of Refunds
- Ensures faster GST refunds for exporters and businesses with input tax accumulation.
- Helps in maintaining positive cash flow and working capital.
Digital Record Maintenance
- GST filing promotes digitized records, reducing paperwork and making tax audits smoother.
- Online filing simplifies return submissions and reduces human errors.
Supports Business Growth
- Compliance with GST laws allows businesses to expand without tax-related obstacles.
- Necessary for applying for government incentives and benefits.
Documents Required for GST Return filings
- Sales & Purchase Invoices – Outward & inward supply details.
- GST Payment Challans – Proof of tax payments.
- Bank Statements – To verify transactions.
- E-way Bills – If applicable for goods transport.
- ITC Documents – Purchase invoices & reverse charge details.
- Taxpayer-Specific Documents – Turnover details for composition/regular taxpayers.
- Other Supporting Documents – GST registration, reconciliations (GSTR-2A/2B).
GST Return Filing Charges in India
Here’s a breakdown for GST Return Filing Charges in India:
Type of GST Return
Professional Fee (Approx.)
GSTR-1 (Monthly/Quarterly Sales Return)
Rs. 500 – Rs. 2,500 per return
GSTR-3B (Monthly Summary Return)
Rs. 500 – Rs. 2,500 per return
GSTR-4 (For Composition Scheme – Annual)
Rs. 1,500 – Rs. 5,000 per return
GSTR-9 (Annual Return – Turnover < Rs. 2 Crore)
Rs. 3,000 – Rs. 8,000 per return
GSTR-9C (Reconciliation Statement – Turnover > Rs. 5 Crore)
Rs. 10,000 – Rs. 30,000 per return
GST Registration
Rs. 3,500 (one-time)
Additional Charges (If Applicable):
- GST Input Reconciliation: Rs. 1,000 – Rs. 5,000
- GST Notices & Response Handling: Rs. 2,000 – Rs. 10,000
- Late Filing Penalty: Rs. 50 per day (Rs. 20 for NIL returns)
GST Compliance Packages:
- Monthly GST Filing (GSTR-1 & 3B) for Small Businesses: Rs. 1,000 – Rs. 5,000
- Annual GST Compliance (Including GSTR-9 & 9C, if required): Rs. 10,000 – Rs. 50,000
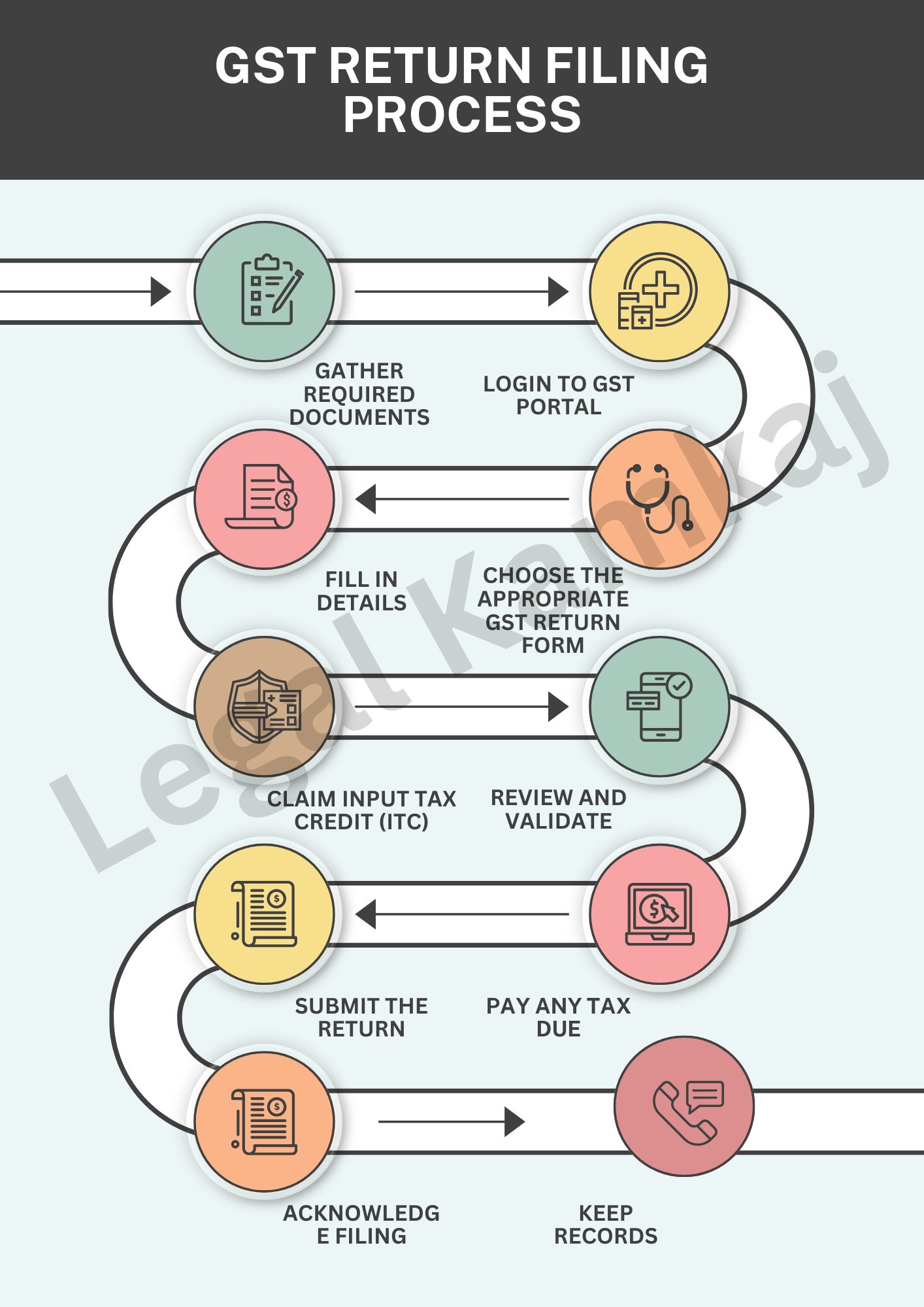
GST Return Filing Process
- Gather Required Documents
- Collect sales, purchase invoices, payment proof, and other relevant documents.
- Collect sales, purchase invoices, payment proof, and other relevant documents.
- Login to GST Portal
- Visit the GST portal and log in using your GSTIN and password.
- Visit the GST portal and log in using your GSTIN and password.
- Choose the Appropriate GST Return Form
- Depending on your business type (e.g., regular, composition), select the appropriate GST return form (e.g., GSTR-1, GSTR-3B).
- Depending on your business type (e.g., regular, composition), select the appropriate GST return form (e.g., GSTR-1, GSTR-3B).
- Fill in Details
- GSTR-1: Report outward supplies (sales) details.
- GSTR-3B: Report summary of sales, purchases, input tax credit (ITC), and tax payable.
- Claim Input Tax Credit (ITC)
- Ensure you report eligible ITC based on purchase invoices to reduce tax liability.
- Ensure you report eligible ITC based on purchase invoices to reduce tax liability.
- Review and Validate
- Double-check the data entered for accuracy.
- Use the “Save” option to save drafts before final submission.
- Pay Any Tax Due
- If taxes are due, make payment through the GST portal using available payment options.
- If taxes are due, make payment through the GST portal using available payment options.
- Submit the Return
- Submit the return once all data is validated.
- Submit the return once all data is validated.
- Acknowledge Filing
- After submission, you will receive an acknowledgment with an ARN (Acknowledgment Reference Number) for tracking.
- After submission, you will receive an acknowledgment with an ARN (Acknowledgment Reference Number) for tracking.
- Keep Records
- Maintain a copy of the filed return and acknowledgment for future reference and audit purposes.
Eligibility Criteria for GST Return Filing
- GST Registration Requirement
- Businesses with a turnover exceeding the prescribed limit must register for GST and file returns.
- The threshold limit varies by business type (e.g., ₹40 lakhs for goods, ₹20 lakhs for services in most states).
- Regular or Composition Scheme
- Regular Scheme: For businesses above the threshold limit.
- Composition Scheme: For smaller businesses (turnover up to ₹1.5 crore) opting for a simplified tax regime with lower rates and easier filing.
- Types of Businesses
- Registered Taxpayers: Must file returns irrespective of turnover.
- E-commerce Sellers: Must comply with GST return filing requirements if registered under GST.
- Exports and Imports
- Exporters must file GST returns, and importers must comply with the Import GST filing.
- Exporters must file GST returns, and importers must comply with the Import GST filing.
- Voluntary GST Registration
- Businesses voluntarily registered for GST must file returns as well.
Types of GST Returns
1. GSTR-1:
- Who files: Regular taxpayers
- Purpose: Details of outward supplies (sales) made during the period.
- Due date: 11th of the next month.
GSTR-2 (Suspended):
- Who files: Regular taxpayers (formerly for purchase details)
- Purpose: Used for reporting inward supplies (purchases) and claiming ITC.
- Note: GSTR-2 is currently suspended, and its data is auto-populated from GSTR-1.
GSTR-3B:
- Who files: All regular taxpayers
- Purpose: Summary of outward supplies, inward supplies, ITC, and tax payable.
- Due date: 20th of the next month.
GSTR-4:
- Who files: Composition scheme taxpayers
- Purpose: Summary of sales, purchases, and tax payable for those under the composition scheme.
- Due date: 18th of the month following the quarter.
GSTR-5:
- Who files: Non-resident foreign taxpayers
- Purpose: Details of supplies made by non-resident taxpayers.
- Due date: 20th of the next month.
GSTR-6:
- Who files: Input Service Distributors (ISDs)
- Purpose: Details of ITC distributed to various branches.
- Due date: 13th of the next month.
GSTR-7:
- Who files: Taxpayers required to deduct TDS (Tax Deducted at Source)
- Purpose: Details of TDS deducted and paid.
- Due date: 10th of the next month.
GSTR-8:
- Who files: E-commerce operators
- Purpose: Details of supplies made through e-commerce platforms and TCS (Tax Collected at Source)
- Due date: 10th of the next month.
GSTR-9:
- Who files: Annual return for regular taxpayers
- Purpose: Summary of all returns filed during the year (GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, etc.).
- Due date: 31st December after the end of the financial year.
GSTR-10:
- Who files: Taxpayers whose GST registration is canceled
- Purpose: Final return after cancellation of GST registration.
- Due date: Within 3 months of cancellation.
GSTR-11:
- Who files: UN bodies or notified persons/entities
- Purpose: Details of supplies and ITC for claiming a refund.
- Due date: 28th of the month following the period.
Checklist for GST Return Filing
Supply Invoices: First and foremost, gather all your supply invoices to establish a clear record of transactions.
GST Refund Details: Next, compile the GST refund details to ensure you include all necessary information.
Comprehensive List of All Tax Invoices: Additionally, create a comprehensive list of all tax invoices, as this will help you keep track of your taxable supplies.
Details Regarding Pending ITC: Furthermore, collect details regarding any pending ITC, since this information is crucial for accurate filings.
Information on Credit Notes or Canceled Sales: Moreover, provide information on credit notes or canceled sales, as this will assist in reconciling your accounts.
Data on Returned Goods: In addition, gather data on returned goods to ensure your records reflect the correct sales figures.
Verification of Credit for Reverse Charge: Simultaneously, verify the credit for reverse charge transactions to maintain compliance with GST regulations.
Cross-Checking Purchase Invoices: After that, cross-check your purchase invoices to confirm that all expenses are accounted for.
Sales Reversed After GST Payment: Additionally, document any sales reversed after the GST payment to ensure accuracy in your reporting.
Information on GST Reversals Related to Purchases: Finally, provide information on GST reversals related to purchases, as this will further ensure that your filing is complete.
FAQ about GST Returns Filing
GST is a comprehensive indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services in India. It replaces multiple indirect taxes with a single tax structure.
All registered GST taxpayers must file returns. This includes businesses and individuals registered under GST, regardless of their turnover.
Late fees and penalties may apply for delayed filing. Additionally, input tax credit may be affected.
GSTR-1 can be revised in the subsequent month’s return. GSTR-3B cannot be revised, but mistakes can be rectified in future returns.
Essential documents include:
- Sales invoices
- Purchase invoices
- Payment vouchers
- Shipping bills
- Any other relevant documents